Science of Reading: Research-based methods that best help children learn to read (Really Great Reading, n.d.). It includes an emphasis on explicit phonics teaching.
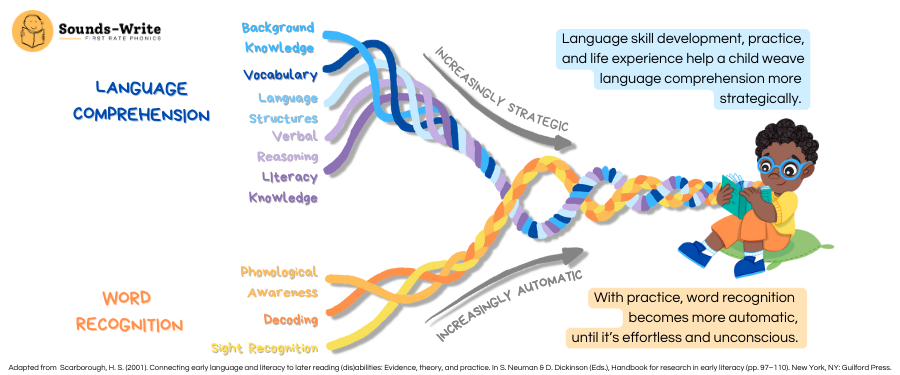
Scarborough’s Reading Rope: Different strands of reading that when interconnected create accurate, fluent reading with comprehension (Really Great Reading, n.d.). The lower strands include phonological awareness, decoding, and sight recognition. The upper strands include background knowledge, vocabulary, language structure, verbal reasoning, and literacy knowledge.
Phonological awareness: Recognizing and manipulating the sounds in spoken words (Reading Rockets, n.d.).
Phonics: Knowing letter sounds and applying it to decoding printed words (Reading Rockets, n.d.).
Print concepts: An understanding that print is organized in a certain way. For example, print is read top to bottom and left to right, and words have letters and spaces (Reading Rockets, n.d.).
Decoding: Sounding out words by using letter-sound relationships to translate printed words into speech (Reading Rockets, n.d.).
Sight word recognition: Words that can be read instantly without sounding them out (Reading Rockets, n.d.).
Fluency: The ability to read a text with accuracy and expression (Reading Rockets, n.d.).
Background knowledge: The amount of information someone has on a topic (Starke, 2021).
Text-to-self, text-to-world, and text-to-text strategies: A connection between the text and your life experience (text-to-self), a connection between the text and something happening in the world (text-to-world), a connection between the text and a previously read text (text-to-text) (Learning for Justice, n.d.).
Vocabulary: Words used for listening, speaking, reading, and writing (Reading Rockets, n.d
Comprehension: The ability to understand something, like a text (Reading Rockets, n.d.).
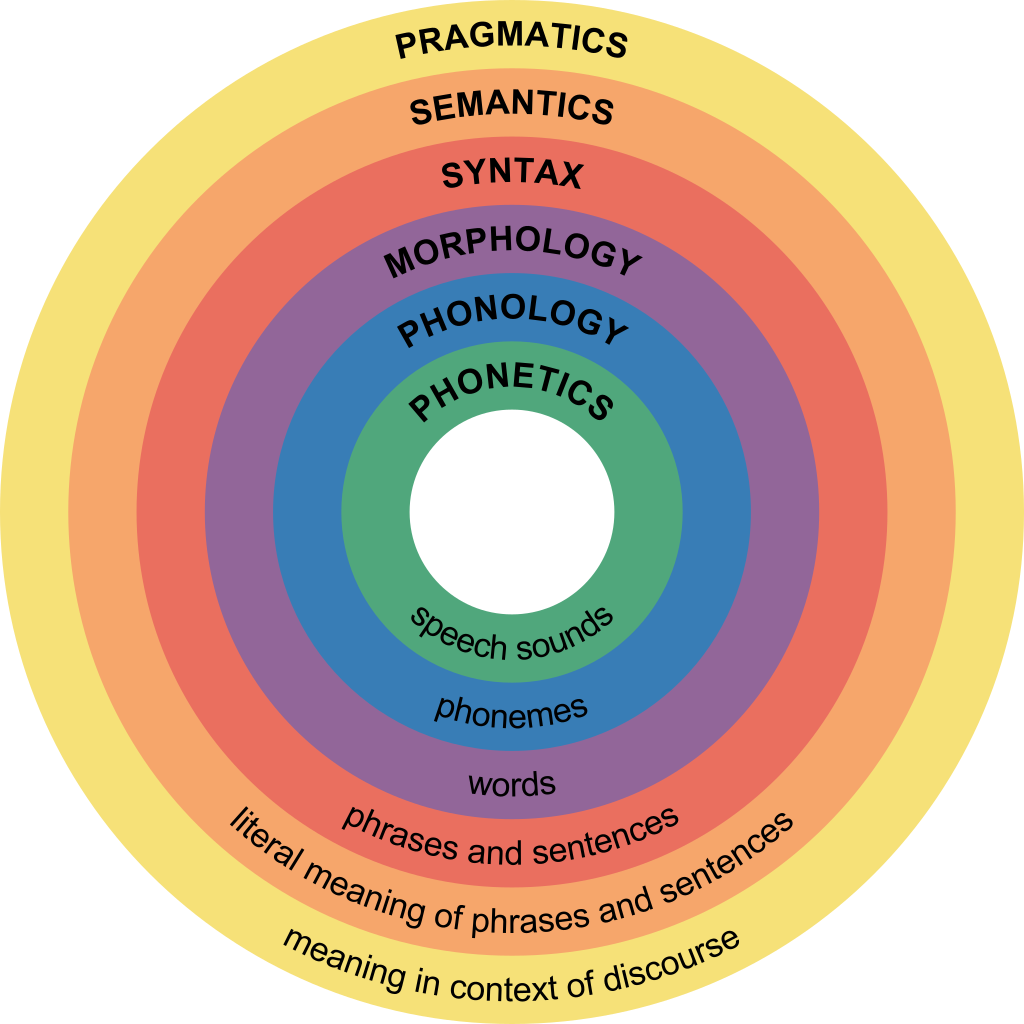
Language structure- How the order of words in sentences impacts the meaning (Surrey Schools ONE, n.d.).
Syntax- The arrangement of words to create sentences that have meaning (Surrey Schools ONE, n.d.).
Semantics- The overall message of a sentence (Surrey Schools ONE, n.d.).
Verbal reasoning- The ability to understand the meaning of a text (Surrey Schools ONE, n.d.).
Literal language- When words mean exactly what they say (Summit Learning, n.d.).
Figurative language- When words are used in a different way than their literal meaning to provoke imagery or feeling (Summit Learning, n.d.).
Literacy knowledge- How printed language conveys meaning (Surrey Schools ONE, n.d.).
Imaginative/Literary text- Stories about people, animals, or events that are made up (Standards Aligned System, n.d.).
Informational/Expository text- Stories that give facts about real people, places, or events (Standards Aligned System, n.d.).




No comments:
Post a Comment